Habitat suitability of Gymnocladus assamicus - A critically endangered plant of Arunachal Pradesh, India using machine learning and statistical modeling
Ujjal Deka BaruahActa Ecologica Sinica , 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2022.05.009

Abstract:
The present study sought to identify the potential distribution range of critically endangered Gymnocladus
assamicus in Arunachal Pradesh based on published data and fild collection. We used the Maxent model to
estimate the range of distribution and the result was then compared with three other models, i.e., the Generalized Linear Model (GLM), the Bioclim and the Random Forest model to assess the species' habitat suitability. A total of 23 different environmental variables were used, including bioclimatic ones, monthly minimum and maximum temperature, monthly precipitation and elevation data. The Maxent output listed 12 variables explaining 99.9% variation in the model. In comparison, Maxent showed the maximum region under habitat suitability criteria (1884.48 km2), followed by Random Forest (70.73 km2) and Bioclim (11.62 km2) model. Except for the Maxent model, suitable habitats predicted by other models are highly restricted within and across the study species' current distribution range. The average model prediction shows an expanded distribution range for the species up to Tawang which is the closest district of currently known distribution of the species in the state. Thus, the present study recognizes the importance of the geographic range of G. assamicus, a critically endangered species with very limited spatial distribution range and also provides some specifi details to explore possible habitats for the species in new areas of potential occurrence in Arunachal Pradesh, India.
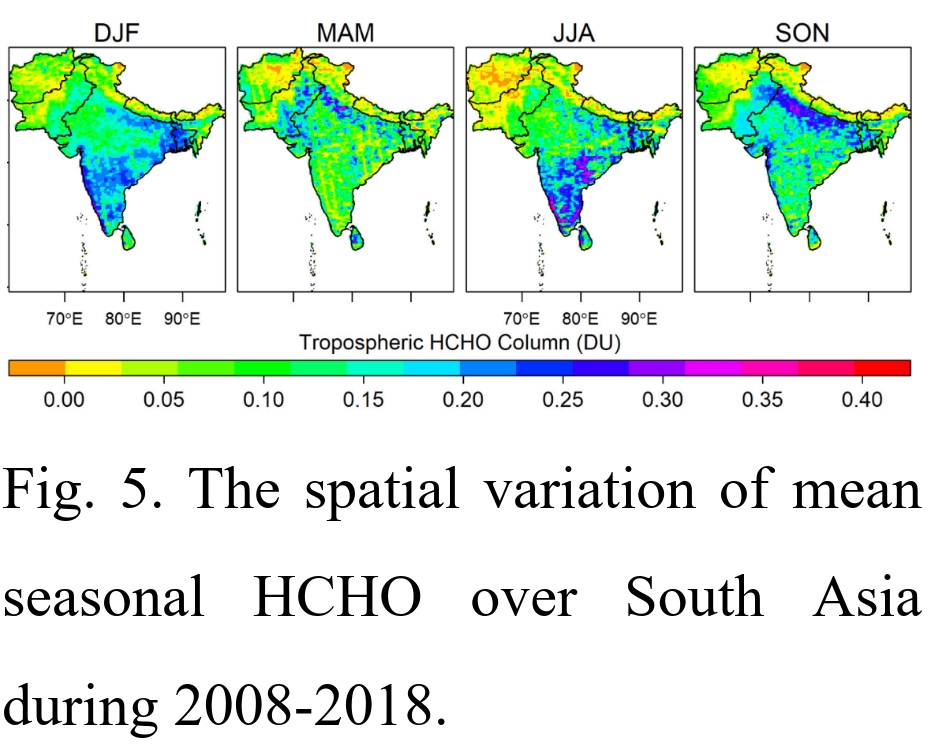
Spatio-temporal characterization of tropospheric ozone and its precursor pollutants NO2 and HCHO over South Asia
Ujjal Deka BaruahScience of The Total Environment , vol: 809 , 151135, 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151135
Abstract:
In recent decades, South Asia has experienced declining air quality, with much of the attention being focused on extremely high levels of particulate matter. Here, we analyze tropospheric ozone (O3), formaldehyde (HCHO), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) to assess other measures of air quality across South Asia from 2008 to 2018. The IASI-Forli retrieved tropospheric ozone data was validated with ozonesonde, reanalysis (ERA5), satellite (TES), and model simulation products (GEOS-Chem and TOMCAT/SLIMCAT). Space-based observations of these three trace gases were used to conduct a spatio temporal analysis over South Asia using trend analysis (Theil-Sen and linear regression), change-point detection (Pettitt's test), and hotspot identification (Getis-Ord Gi*). We used the formaldehyde-nitrogen dioxide ratio (FNR) to identify NOx limited, VOC limited, and transitional regimes in South Asia. Counter to previous studies, a statistically significant decrease of HCHO (−0.0041 DU yr−1) and O3 (−0.064 DU yr−1) was detected for South Asia; however, NO2 is increasing the 0.001 DU yr−1 over South Asia during 2008–18. The Indo-Gangetic Plains emerged as being critically affected by the three trace gases. Certain parts of southern and south-eastern India are gradually emerging as NO2 and HCHO hotpots. No significant O3 hotspots were discernible, though coldspots existed along the Himalaya belt of India, Nepal, and Bhutan and mountainous tracts of Pakistan. FNR indicates the reduction of NOx in NOx-limited regime of the Indo-Gangetic Plains reduced the formation of tropospheric O3 over South Asia.
Distress Migration and Involuntary Return During Pandemic in Assam: Characteristics and Determinants
Girimallika BorahIndian Journal of Labour Economics , 2022 , doi.org/10.1007/s41027-022-00392-8
Abstract:
Spatial Distribution and Trend Estimation of Tropospheric Formaldehyde: A Space-Borne Observation Over South Asia
Ujjal Deka Baruah & Nitashree MiliEnvironmental Change in South Asia , 171-185, 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-47660-1_9
Abstract:
This chapter deals with the distribution and recent changes of tropospheric formaldehyde as measured from space borne sensors aboard Aura/OMI satellite of 0.1° × 0.1° spatial resolution during 2008–2018 over South Asia. The concentration of formaldehyde is mainly concentrated in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of South Asia spanning Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Thiel-Sen’s analysis indicates a decreasing trend (−0.004 DUyr−1) during the study period.
When the Bough Breaks: Spatial Variability of Tropospheric Ozone in the Indian Sub-continent
Ujjal Deka BaruahIn: Saikia, A., Thapa, P. (eds) Environmental Change in South Asia. Springer, Cham , 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-47660-1_11
Abstract:
Tropospheric or ground level ozone (O3) is an important greenhouse gas and a pollutant harmful to human health and agricultural activity. With high population pressure in the Indian Sub-continent and economies heavily reliant on agriculture and allied activities tropospheric ozone is problematic. This analysis assesses the spatial variability of tropospheric ozone using monthly AIRX3STM satellite data during 2002–16. The monthly images were combined and averaged to derive month-wise and four season-wise aggregates during 2002–2016 in order to understand monthly and seasonal variations in the spatial patterns of O3. A gain coefficient image was also generated using a GIS to visualize and depict areas with spatial variability of O3 during the period.
Agro-Climatic Constraints and the Adaptive Empirical Knowledge System of Indigenous Farmers in Assam, India
Ujjal Deka BaruahTraditional Ecological Knowledge of Resource Management in Asia , 333–348, 2023 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16840-6_20
Abstract:
There exists a symbiotic relationship between climate change, farmers, and crops. Assam has faced innumerable floods and sporadic drought-like situations since time immemorial. This chapter deals with the inter-relationship among the variables and assesses the constraints in agriculture and indigenous farmers’ knowledge system of adaptation measures to cope with climate change. Erosion and sedimentation that are a fallout of flooding have adversely affected the agricultural landscape in some areas of Assam. A survey was carried out in five agro-ecological zones of Assam to assess the agro-climatic constraints and farmers’ ecological knowledge systems. India Meteorological Department (IMD) data (1971–2011) was used to evaluate the climatic variability and change in Assam. Assam witnessed changes in the main crop or varieties of crops like the change of total cropped area under winter (“Sali”) rice, etc. On the other hand, peanuts, jute, pulses, maize, sugarcane, and watermelon were introduced. A gradual rise in area under boro rice followed by a decrease in area under sali and autumn rice set in. In some parts of Central Brahmaputra Valley close to Brahmaputra River and its tributaries and the North Bank Plain Zone, farmers chose to replace the main crops sali rice (summer crop), and adopt “bao” rice (a water-resistant local rice breed) or oilseeds due to the vagaries of climate.
Distribution mapping of five threatened medicinally important plant species of Arunachal Himalaya
Kuladip Sarma,.., Ujjal Deka BaruahVegetos , 2023 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-023-00619-z
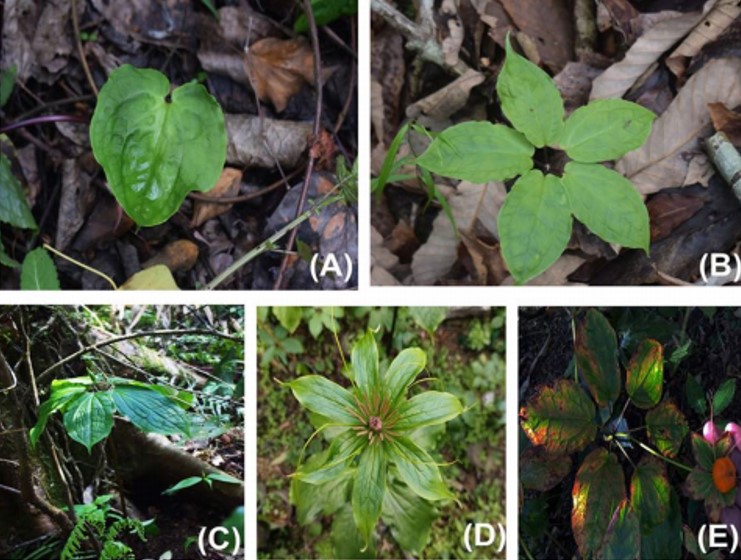

Abstract:
Eastern Himalaya, one of the major hubs of plant diversity, is home to numbers of rare, endangered, and threatened plant species in general. The present study aims to study five selected threatened plant species found in Arunachal Pradesh, India for its distribution and potential habitat identification. An extensive field survey was carried out in the various pockets of the state of Arunachal Pradesh from March 2020 to July 2022, collecting GPS locations of five selected threatened plants viz., Paris polyphylla, Coptis teeta, Gymnocladus assamicus, Taxus wallichiana, and Amentotaxus assamica. A machine learning approach was adopted for mapping the diversity and endemism of these species in the study area. A machine learning approach was adopted for predicting the potential distribution of the five threatened species and then the high potential areas were combined to create a priority conservation area for all the species together. A total of 505 individuals of the five species were found in 108 locations in four districts of Arunachal Pradesh, India. The highest number of individuals was recorded for the species C. teeta spread over 20 different locations and the lowest was recorded for G. assamicus (18 individuals) in only 8 locations. The current distribution of five selected threatened plants in Arunachal Pradesh reveals an overlap in the geographic range of these species. The mapping of the distribution of five different important plant species enabled us to know the overall diversity patterns of these selected plants and would be helpful in the formulations of appropriate conservation strategies.
Urban livability and contextual uncertainties: An assessment of livability through the lens of urban dwellers in Guwahati, India
Anwesha Mahanta, Parijat BorgohainJournal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development, Singapore , vol: 6 , 2022 , 1395
Abstract:
Sustainable Ethnic Tourism Development in Arunachal Pradesh
Parijat Borgohain, Barnali Patowary/ Edited by Subhash Anand, Madhushree Das, Rituparna Bhattacharyya, R.B. Singh, published by SpringerSustainable development goals in North East India : Challenges and Achievements, International Geographical Union (IGU) Series: Advances in Environmental and Geographical Sciences, Springer Nature , 489-506, 2023
Abstract:
Influence of Namghars in Assamese Society of Barpeta District of Assam
Shrabani Devi, Parijat BorgohainShodh Sarita , vol: 8 , 144-148, 2021
Abstract:
Management of Namghar in Assam
Shrabani Devi, Parijat BorgohainShodh Sanchar , vol: 11 , 166-169, 2021
Abstract:
Wellbeing in the aftermath of floods: Findings from a qualitative study in Bongaigaon District of Assam, India
Girimallika Borah, Nandita Saikia, Shyamanta Das, and Sanjeev SharmaWellbeing, Space and Society , 2023 , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wss.2023.100147
Abstract:
GIS‑based revised universal soil loss equation for estimating annual soil erosion: a case of lower Kulsi basin, India
Gitika ThakuriahSN Applied Sciences , vol: 5 , 2023 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-023-05303-0
Abstract:
Geographic information system and analytical hierarchical process approach for groundwater potential zone of lower Kulsi basin, India
Gitika ThakuriahSustainable Water Resources Management (2023) 9:85 , vol: 9 , 2023 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00870-x
Abstract:
Geospatial and. Analytical Hierarchical Process approach for potential ssiyrs of water harvesting in lower Kilsi basin, India
Gitika ThakuriahGeoScape , vol: 17 , 58-73, 2023 , https://doi.org/10.2478/geosc-2023-0005
Abstract:
Environmental Status and Changing Landuse/Landcover of Kapla Beel in Barpeta District, Assam
Anjan Deka and Mala DuttaInternational Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews , vol: 6 , 314-322, 2019
Abstract:
Crop Productivity Zones in Assam: A Geospatial Analysis
Mala Dutta and Sahil ChaudhuryNorth Eastern Geographer , vol: 42 , 78-90, 2022
Abstract:
E-Waste Generation, Awareness and Management Policies in Higher Educational Institutions: A Case Study from Cotton University, Assam
Mala Dutta and Rani Kumari ShahIndian Journal of Natural Sciences , vol: 14 , 65897-65906, 2023
Abstract:
Status of Horticulture in Lakhimpur District of assam with Special reference to Laluk and Narayanpur ADO Circle
Pranamika Bora, Mala Dutta and Rani Kumari ShahIndian Journal of Natural Scinces , vol: 14 , 2024
Abstract:
Agricultural Landuse and Productivity in North-East India
Jayeeta Tamuli and Mala DuttaRecent Advances in Social Science Research: In the Context of India's North-East, Gogoi, Saikia (Eds) , 64-80, 2023
Abstract:
Changing Population Dynamics, Losses and Adaptation to Recurring Floods in Bongaigaon
Girimallika Borah and Nandita SaikiaIn: Biswas, B., Ghute, B.B. (eds) Flood Risk Management. Springer Natural Hazards. Springer, Singapore. , 2024 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2688-2_7
Abstract:
Population Dynamics of the Ecologically Challenged Riverine Islands in the Brahmaputra River of assam: A Case Study of Chaprapara Char
Abul Fazal Murtaza Ahmed, Parijat BorgohainNorth Eastern Geographer , vol: Vol.42 No.1&2 , 116-131, 2023
Abstract:
Population Dynamics of the Ecologically Challenged Riverine Islands in the Brahmaputra River of assam: A Case Study of Chaprapara Char, Abul Fazal Murtaza Ahmed, Parijat Borgohain in North Eastern Geographer, Vol.42 No.1&2, ISSN 0973-0915, pp. 116-`131, 2022-2023
Role of Lokapriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport in Changing the Socio- economic condition of the surrounding area
Saswata Saharia and Mala DuttaHumanities and Social Science Studies, , vol: 12 , 2023
Abstract:
A Study on Farmers Producer Company with Special Reference to Suntali Maize Producer Company in Rajamayang, Morigaon District, Assam, India
Mayuri Sarma, Mala Dutta and Rani Kumari ShahEcology Environment and Conservation , vol: 30 , S405-S410, 2024 , http://doi.org/10.53550/EEC.2024.v30i05s.062
Abstract:
Characteristics of Positive and Negative Mortality Outlier States in India
Girimallika BorahMan & Development , vol: XLIV , 101-116, 2024
Abstract:
Spatial Distribution and Characteristics of Wetlands in Dibrugarh District, Assam: a GIS Based Approach
Rani Kumari Shah and Mala DuttaProceedings of the Indian National Science Academy , 2024 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s43538-024-00383-x
Abstract:
Effect of 'losses' and other secondary stressors on the association between flooding and psychological health outcomes: a cross-sectional study in Bongaigaon District, India
Girimallika Borah and Nandita SaikiaJournal of Biosocial Sciences, Cambridge University Press , 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021932025000136
Abstract:
Flood Susceptibility Assessment of Dibang Valley District of Arunachal Pradesh, India: A GIS based Analytic Hierarchy Process Approach
Rani Kumari Shah, Deepjyoti Bhattacharjya, Bikash Jyoti Gautam, Mala Dutta, Rajesh Kumar ShahRemote Sensing in Earth Systems Sciences , vol: 8 , 996-1013, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s41976-025-00232-5
Abstract:
Women Leading the Green Movement: Ecofeminist Efforts in Assam
Rishee Gogoi, Mala Dutta and Rani Kumari ShahGuineis Journal , vol: 12 , 149-164, 2024
Abstract:
Constructing a City Liveability Index and Evaluating the Spatial Pattern of Liveability of Guwahti City
Anwesha Mahanta, Dr. Parijat Borgohain,Visnyk of V.N. Karazin Kharkiv National University. Series. Geology. Geography. Ecology , 2025 , 10.26565/2410-7360-2025-62-19
Abstract:
A Spatial Pattern Of Population Growth And Urban Development In Dibrugarh City, Assam
Suntoo Das, Mala DuttaInternational Journal of Environmental Sciences , vol: 11 , 1957-1968, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.64252/0gvmga51
Abstract:
Land use Land Cover Dynamics and Fragmentation in Dimoria Block, Assam: A Geospatial Assessment
Sahul Choudhury and Mala DuttaEcology, Environment and Conservation , vol: 31 , S151-S165, 2025 , http://doi.org/10.53550/EEC.2025.v31i07s.025
Abstract:
Traditional Health Care Practices of the Wancho Tribe of Arunachal Pradesh, India
Shiv Ram Dev Gauri , Rani Kumari Shah, Rajesh Kumar Shah and Mala DuttaEncyclopedia of Disaster Risk Reduction, , 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-4547-0_225-1
Abstract:
Channel Dynamics and Bankline Shift of the Brahmaputra River in Morigaon District, Assam
Ananya Saikia, Monjit Borthakur and Barnali GogoiDisaster Advances , vol: 18 , 60-80, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.25303/189da060080
Abstract:
Geochemical Characteristics of Metasomatised Diorites in and around Umsopri of Ri-bhoi District, Meghalaya, India
Dr. Anamika Gogoi and Dr. Balen BhagabatyJournal of Geography, Environment and Earth Science International , vol: 15 , 1-14, 2018
Abstract:
Mineral Chemistry and Geothermometry of Biotite in the Granitoids , Located in and around Jirang -Patharkhamah Area,Ri-Bhoi District,Meghalaya,India
Dr. Anamika Gogoi and Dr. Balen BhagabatyJournal of the Geological Society of India , vol: 98 , 245–259, 2022
Abstract:
Reservoir characterization and rock eval pyrolysis of clastic sedimentary rocks in the Geku Formation, Arunachal Pradesh, North-eastern India
Bordoloi, A., Chutia, A., & Taye, C. D.Journal of The Indian Association of Sedimentologists , vol: Vol-40 (I) , 43–54, 2023 , https://doi.org/10.51710/jias.v40iI.284
Abstract:
Petrography and clay mineral study of Siwalik Group, East Siang District, Arunachal Pradesh: Implications for tectonic setting and depositional environment
Chutia, A., Gogoi, M. P., Taye, C. D., and Bordoloi, A., 2022Indian Journal of Geosciences , vol: Vol-76 (4) , 371-384, 2022
Abstract:
Petrography and geochemistry of Palaeogene sandstones of Geku Formation, Yinkiong Group, Arunachal Pradesh, NE India: implications on provenance and tectonic setting
Bordoloi, A, Chutia, A., Taye, C. D. and Gogoi, M. PJournal of Sedimentary Environments , vol: 7 (4) , 691-709, 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-022-00116-4
Abstract:
Provenance of the Yinkiong Group exposed along Pasighat-Mariyang Road section, East Siang District, Arunachal Pradesh: A petrographic, heavy mineral and clay mineralogical approach
Chutia, A., Taye, C. D., Nath, D., and Chutia, D., 2019Indian Journal of Geosciences , vol: 73 (4) , 253-264, 2019
Abstract:
Petrography of Tipam Sandstone Formation of Miocene Age from Upper Assam Basin, India- A Compositional and Diagenetic Approach to Decipher the Sedimentation History
Chutia, A and Sarma J.N., 101-115, 2021
Abstract:
A novel technique for temporal evolution of rockburst in underground rock tunnel: an experimental study
Das R, Singh TNEnvironmental Earth Sciences , vol: 81 , 420, 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10546-y
Abstract:
Geotechnical Insights of the Cut Slopes Along Silchar-Haflong National Highway, Assam, India
Das R, Singh TNGeotechnical and Geological Engineering , vol: 42 , 6195–6217, 2024 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-024-02892-4
Abstract:
Significance of viscous folding in the migmatites of Chotanagpur Granite Gneiss Complex, eastern India
Bibhuti Gogoi, Hiredya Chauhan, Gaurav Hazarika, Amiya Baruah, Mukunda Saikia, Pallab Jyoti HazarikaEarth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh , vol: 111 , 119-134, 2020 , https://doi.org/10.1017/S1755691020000067
Abstract:
Cold Plumes Initiated by Rayleigh‐Taylor Instabilities in Subduction Zones, and Their Characteristic Volcanic Distributions: The Role of Slab Dip
Dip Ghosh, Giridas Maiti, Nibir Mandal, Amiya BaruahJournal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth , vol: 125 , e2020JB019814, 2020 , https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB019814
Abstract:
Optimal Softening for Gravitational Force Calculations in N-body Dynamics
H Das, S Deb, A BaruahThe Astrophysical Journal , vol: 911 , 83, 2021 , DOI 10.3847/1538-4357/abe94d
Abstract:
Ensemble-based unsupervised machine learning method for membership determination of open clusters using Mahalanobis distance
S Deb, A Baruah, S KumarMonthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , vol: 515 , 4685-4701, 2022 , https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stac2116
Abstract:
Reaction-diffusion modelling of petrological mixing mechanisms in the evolution of continental crusts
A Baruah, MK Roy, N Mandal, S MisraFrontiers in Earth Science , vol: 11 , 1115103, 2023
Abstract:
Ground surface displacements and stress localization driven by dual magma chamber dynamics: analytical and numerical model estimates
PJ Hazarika, R Dasgupta, A Baruah, N MandalInternational Journal of Earth Sciences , 1-20, 2024
Abstract:
Provenance and depositional setting of the Disang Group exposed in the north‑easternmost part of Assam‑Arakan Basin, India: insights from petrography and clay mineralogy
Dimple Moni Kachari, Chaitra Dhar Taye and Ananya ChutiaJournal of Sedimentary Environments , 2024 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-024-00199-1
Abstract:
Catastrophic landslide in Wayanad district of Kerala, India on July 30, 2024: A complex interplay between geology, geomorphology, and climate
Das RLandslides , vol: 22 , 271-281, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-024-02385-8
Abstract:
Classifying rock types by geostatistics and random forests in tandem
Parag Jyoti Dutta and Xavier EmeryMachine Learning: Science and Technology , vol: 5 , 1 - 25, 2024 , https://doi.org/10.1088/2632-2153/ad3c0f

Abstract:
Rock type classification is crucial for evaluating mineral resources in ore deposits and for rock mechanics. Mineral deposits are formed in a variety of rock bodies and rock types. However, the rock type identification in drill core samples is often complicated by overprinting and weathering processes. An approach to classifying rock types from drill core data relies on whole-rock geochemical assays as features. There are few studies on rock type classification from a limited number of metal grades and dry bulk density as features. The novelty in our approach is the introduction of two sets of feature variables (proxies) at sampled data points, generated by geostatistical leave-one-out cross-validation and by kriging for removing short-scale spatial variation of the measured features. We applied our proposal to a dataset from a porphyry Cu–Au deposit in Mongolia. The model performances on a testing data subset indicate that, when the training dataset is not large, the performance of the classifier (a random forest) substantially improves by incorporating the proxy features as a complement to the original measured features. At each training data point, these proxy features throw light based on the underlying spatial data correlation structure, scales of variations, sampling design, and values of features observed at neighboring points, and show the benefits of combining geostatistics with machine learning.
Soil Erosion Estimation of Palasbari in Northeast India by RUSLE Model
Karishma Sarma and Parag Jyoti DuttaBulletin of Pure and Applied Sciences-Geology , vol: 40 , 129-141, 2021 , https://doi.org/10.5958/2320-3234.2021.00012.3
Abstract:
Soil erosion is a serious problem and its estimation at a large scale is an urgent need. This study aims to estimate the annual soil loss in Palasbari town (639 km2) applying the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model on a GIS platform. The study area comprising Palasbari town is located in the state of Assam in Northeast India. The annual soil loss rate varies from 0 to 3779t ha-1 yr-1 and the mean annual rate of soil loss is 42 t ha-1 yr-1. The soil loss values are categorised into four classes of severity i.e. slight, moderate, severe and extreme soil erosion. Based on spatial analysis, it is found that areas with high slope length and steep slope with heavy and high intensity precipitation are more prone to soil erosion. It is concluded that steep slopes, frequent flooding, sandy soil, destruction of vegetation cover are the main causes of soil erosion in the study area.
A Field Verification Based Statistical Approach toward Landslide Susceptibility Assessment
Parag Jyoti Dutta, Jayanta Jivan Laskar, and Santanu SarmaBulletin of Pure and Applied Sciences-Geology , vol: 38 , 266-273, 2019 , https://doi.org/10.5958/2320-3234.2019.00020.9
Abstract:
Predicting the Spatial Distribution of Rain-Induced Shallow Landslides by applying GIS and Geocomputational Techniques: A Case Study from North East India
Parag Jyoti Dutta, Santanu Sarma, Jayanta Jivan LaskarInternational Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication , vol: 5 , 1306–1319, 2017 , https://doi.org/10.17762/ijritcc.v5i5.698
Abstract:
Nonlinear regression technique to assess the landslide susceptibility of the Kalapahar hill, Guwahati, Assam State (India)
Maria Giuseppina Persichillo, Parag Jyoti Dutta, Massimiliano Bordoni, Claudia Meisina, Carlotta Bartelletti, Michele Barsanti, Roberto Giannecchini, Giacomo D'Amato Avanzi, Yuri Galanti & Andrea CevascoRENDICONTI ONLINE DELLA SOCIETÀ GEOLOGICA ITALIANA , vol: 41 , 179-182, 2016 , https://doi.org/10.3301/ROL.2016.123
Abstract:
Laboratory Simulation of Rockfall Hazard in Different Sedimentary Rocks of Mizoram, India
Mazumder D, Das R, Das SProceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Geotechnical Issues in Energy, Infrastructure and Disaster Management. ICGEID 2024. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering , vol: 475 Springer, Singapore , 77-92, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-1757-6_7
Abstract:
Tunnelling in squeezing ground – a review on prediction and measurement of boundary deformation and available mitigation methods
Das R5th International Disaster Risk and Vulnerability Conference (DVRC 2023). K. R. Baiju, Karunakaran Akhildev, Joice K Joseph, Naveen Babu, Anithomas Idiculla, Asha Rose, Shibu K Mani, Mahesh Mohanand A.P. Pradeep Kumar (Eds) 19-21 Jan 2023, Kerela, India , 2023 , Link
Abstract:
Understanding the cause and effect relationship of debris slides in Papumpare district, Arunachal Himalaya, India
Das R, Phukon P, Singh TNNatural Hazards , vol: 110 , 1735-1760, 2021 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-05010-2
Abstract:
Analysis and prediction of brittle failure in rock blocks having a circular tunnel under uniaxial compression using acoustic Emission technique: laboratory testing and numerical simulation
Das R, Dhouchak R, Singh TNInternational Journal of Geo-Engineering , vol: 12 , 2021 , https://doi.org/10.1186/s40703-020-00136-x
Abstract:
Effect of Rock Bolt Support Mechanism on Tunnel Deformation in Jointed Rockmass: A Numerical Approach
Das R, Singh TNUnderground Space , vol: 6 , 409-420, 2021 , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2020.06.001
Abstract:
Effect of Closely Spaced, Non-Persistent Ubiquitous Joint on Tunnel Boundary Deformation: A Case Study from Himachal Himalaya
Das R, Singh TNGeotechnical and Geological Engineering , vol: 39 , 2447–2459, 2020 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01637-3
Abstract:
Comparative study of the deformation modulus of rock mass - a reply to the comments received from Gokceoglu (2018)
Panthee S, Singh PK, Kainthola A, Das R, Singh TNBulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment , vol: 77 , 763-766, 2018 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1272-z
Abstract:
Numerical analysis of surface subsidence in asymmetric parallel highway tunnels
Das R, Singh PK, Kainthola A, Panthee S, Singh TNJournal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering , vol: 9 , 170-179, 2017 , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.11.009
Abstract:
Effect of Water Saturation on the Fracture and Mechanical Properties of Sedimentary Rocks
Guha Roy D, Singh TN, Kodikara J, Das RRock Mechanics and Rock Engineering , vol: 50 , 2585-2600, 2017 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1253-8
Abstract:
Comparative study of the deformation modulus of rock mass
Panthee S, Singh PK, Kainthola A, Das R, Singh TNBulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment , vol: 77 , 751-760, 2016 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0974-3
Abstract:
Runout Characteristics of Rainfall-Induced Debris Flow: A Case Study from Sonapur, Meghalaya, India
Das S, Das R, Mazumder DGeotechnical and Geological Engineering , vol: 43 , 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-025-03078-2
Abstract:
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Framework for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping With Analytical Hierarchy Process in Parts of Assam–Arakan Fold Belt, India
Mazumder D, Das R, Das SGeological Journal , 1-16, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.5229
Abstract:
Understanding the landslide trigger mechanism in gently dipping shale beds: A case study from Aizawl, Mizoram, India
Mazumder D, Das R, Das S, Singh TNJournal of Earth System Science , vol: 134 , 1-18, 2025 , https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-025-02647-6
Abstract:

